Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takahashi, Nobuaki*; Murata, Hirohiko*; Mitsubori, Hitoshi*; Sakuraba, Junji*; Soga, Tomohiro*; Aoki, Yasushi*; Kato, Takanori*; Saito, Yuichi; Yamada, Keisuke; Ikenaga, Noriaki*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02C306_1 - 02C306_3, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.24(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Kurashima, Satoshi; Okumura, Susumu
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02A735_1 - 02A735_5, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.24(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kojima, Atsushi; Hanada, Masaya; Yoshida, Masafumi; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Grisham, L. R.*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02B312_1 - 02B312_5, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:48.5(Instruments & Instrumentation)The negative ion source for JT-60SA is designed to produce high power and long pulse beams with a beam energy of 500 keV, a negative ion current of 22A and a pulse duration of 100s. One of the key issues toward long pulse production of such high-current beams is the control of the surface temperature on the plasma grid (PG) where cesium is layered. In order to optimize cesium layer on PG for long pulse duration, we have developed an actively cooled PG where fluorinated fluids having high boiling point of 270 C is circulated. While the surface temperature of the PG in the JT-60 negative ion source has been kept at 170
C is circulated. While the surface temperature of the PG in the JT-60 negative ion source has been kept at 170 C for 100s with ramp-up time of 7s, stable long pulse beam extractions of 100s have been obtained. This current density is 90% of the required current density for JT-60 SA. The further increase of the current density is expected by optimizing the arc discharge power.
C for 100s with ramp-up time of 7s, stable long pulse beam extractions of 100s have been obtained. This current density is 90% of the required current density for JT-60 SA. The further increase of the current density is expected by optimizing the arc discharge power.
Yoshida, Masafumi; Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Grisham, L. R.*; Akino, Noboru; Endo, Yasuei; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Nemoto, Shuji; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02B314_1 - 02B314_4, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:50.88(Instruments & Instrumentation)Non-uniformity of the negative ion beams in the JT-60 negative ion source was improved by modifying an external magnetic field to a tent-shaped magnetic field for reduction of the local heat loads in the source. Distributions of the source plasmas (H ions and H
ions and H atoms) of the parents of H
atoms) of the parents of H ions converted on the cesium covered plasma grids were measured by Langmuir probes and emission spectroscopy. Beam intensities of the H
ions converted on the cesium covered plasma grids were measured by Langmuir probes and emission spectroscopy. Beam intensities of the H ions extracted from the plasma grids were measured by IR camera from the back of the beam target plate. The tent-shaped magnetic field prevented the source plasmas to be localized by B
ions extracted from the plasma grids were measured by IR camera from the back of the beam target plate. The tent-shaped magnetic field prevented the source plasmas to be localized by B  grad B drift of the primary electrons emitted from the filaments in the arc chamber. As a result, standard derivation of the H
grad B drift of the primary electrons emitted from the filaments in the arc chamber. As a result, standard derivation of the H ions beams was reduced from 14% (the external magnetic field) to 10% (the tent-shaped magnetic field) without reduction of an activity of the H
ions beams was reduced from 14% (the external magnetic field) to 10% (the tent-shaped magnetic field) without reduction of an activity of the H ion production.
ion production.
Kurashima, Satoshi; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Yoshida, Kenichi; Okumura, Susumu
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02A725_1 - 02A725_3, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)The JAEA AVF cyclotron accelerates various kinds of high energy ion beams for research in biotechnology and materials science. Beam intensity of an ion species of the order of 10 to 10
to 10 ampere is often required for various experiments sequentially performed within a day. To provide the ion beam sufficiently and stably, an operator has to retune an ion source in a short time. The beam intensity downstream of the cyclotron, however in most cases, doesn't increase proportionally to the intensity at the ion source. To understand the cause of this beam behavior, transmission efficiencies of a
ampere is often required for various experiments sequentially performed within a day. To provide the ion beam sufficiently and stably, an operator has to retune an ion source in a short time. The beam intensity downstream of the cyclotron, however in most cases, doesn't increase proportionally to the intensity at the ion source. To understand the cause of this beam behavior, transmission efficiencies of a  C
C beam from the ion source through the cyclotron were measured for various conditions of the ECR ion source. Moreover, a feasible region for acceleration in the emittance of the injection beam was clarified using a transverse-acceptance measuring system. We confirmed that the beam emittance and profile changed depending on the condition of the ion source and the matching between the emittance and the acceptance of the cyclotron got worse. After fine-tuning to improve the matching, the beam intensity downstream of the cyclotron increased.
beam from the ion source through the cyclotron were measured for various conditions of the ECR ion source. Moreover, a feasible region for acceleration in the emittance of the injection beam was clarified using a transverse-acceptance measuring system. We confirmed that the beam emittance and profile changed depending on the condition of the ion source and the matching between the emittance and the acceptance of the cyclotron got worse. After fine-tuning to improve the matching, the beam intensity downstream of the cyclotron increased.
Yoshida, Kenichi; Nara, Takayuki; Saito, Yuichi; Yokota, Wataru
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02A917_1 - 02A917_3, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.77(Instruments & Instrumentation)Recent studies about ECRIS have revealed that not only the maximum magnetic field (B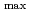 ) but also the minimum field(B
) but also the minimum field(B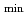 ) has effect on the production ability. A superconducting ECRIS which can change the B
) has effect on the production ability. A superconducting ECRIS which can change the B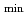 distribution with plural solenoids shows that a flat distribution of B
distribution with plural solenoids shows that a flat distribution of B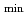 (flat B
(flat B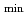 ) gives better performance in highly charged ion production than classical B
) gives better performance in highly charged ion production than classical B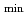 . Superconducting device of conduction cooling type is useful, because a Lq-helium system needs a large quantity of Lq-helium to be supplied at after every quench. However, many refrigerators are necessary to keep low temperature against the heat through the current leads of a number of coils to form flat-B
. Superconducting device of conduction cooling type is useful, because a Lq-helium system needs a large quantity of Lq-helium to be supplied at after every quench. However, many refrigerators are necessary to keep low temperature against the heat through the current leads of a number of coils to form flat-B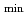 . Therefore, we have designed a coil configuration which can adjust B
. Therefore, we have designed a coil configuration which can adjust B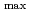 and flat-B
and flat-B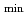 with the minimum lead number of four. The flat-B
with the minimum lead number of four. The flat-B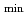 is formed by three central coils connected one another between the mirror coils. There is another pair of coils to adjust B
is formed by three central coils connected one another between the mirror coils. There is another pair of coils to adjust B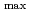 of the injection side keeping flat B
of the injection side keeping flat B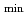 unchanged.
unchanged.
Yamada, Keisuke; Saito, Yuichi; Yokota, Wataru
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02A920_1 - 02A920_3, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.77(Instruments & Instrumentation) ion beams for ITER NB accelerator
ion beams for ITER NB acceleratorUmeda, Naotaka; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Dairaku, Masayuki; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Inoue, Takashi; Kojima, Atsushi; Hanada, Masaya
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02B304_1 - 02B304_3, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:48.5(Instruments & Instrumentation)In order to realize neutral beam systems in ITER whose target is to produce D ion beam of 1 MeV, 200 A/m
ion beam of 1 MeV, 200 A/m during 3600s, the electrostatic five-stages negative ion accelerator has been developed at JAEA. To extend pulse length, heat load of the acceleration grids was reduced by controlling the ion beam trajectory. Namely, the beam deflection due to the residual magnetic filter in the accelerator was suppressed with the newly developed extractor with a 0.5 mm off-set aperture displacement. The use of new extractor improved the deflection angle from 6 mrad to 1 mrad, resulting in the reduction of direct interception of negative ions from 23% to 15% of the total acceleration power, respectively. As a result, the pulse length of 130 A/m
during 3600s, the electrostatic five-stages negative ion accelerator has been developed at JAEA. To extend pulse length, heat load of the acceleration grids was reduced by controlling the ion beam trajectory. Namely, the beam deflection due to the residual magnetic filter in the accelerator was suppressed with the newly developed extractor with a 0.5 mm off-set aperture displacement. The use of new extractor improved the deflection angle from 6 mrad to 1 mrad, resulting in the reduction of direct interception of negative ions from 23% to 15% of the total acceleration power, respectively. As a result, the pulse length of 130 A/m , 881 keV H
, 881 keV H ion beam has been successfully extended from a previous value of 0.4s to 8.7s.
ion beam has been successfully extended from a previous value of 0.4s to 8.7s.
Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Kojima, Atsushi; Yoshida, Masafumi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Dairaku, Masayuki; Maejima, Tetsuya; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02B320_1 - 02B320_3, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:75.28(Instruments & Instrumentation)The negative ion extractor for high power and long-pulse operations is newly developed toward the neutral beam injector (NBI) for heating & current drive of future fusion machines such as ITER, JT-60 Super Advanced (SA) and DEMO reactor. The satisfactory cooling capability is designed in the thermal analysis. A negative ion production and a suppression of electrons are experimentally validated for this new extractor. As the results, the negative ion current shows increases by a factor of 1.3 with suppressing the electron current. The beam divergence angle is also maintained small enough, 4 mrad.
 ion source
ion sourceUeno, Akira; Koizumi, Isao; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Yamazaki, Saishun; Oguri, Hidetomo
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02B133_1 - 02B133_5, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.22(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 ion source for cyclotrons
ion source for cyclotronsEto, Haruhiko*; Aoki, Yasushi*; Mitsubori, Hitoshi*; Arakawa, Y.*; Mitsumoto, Toshinori*; Yajima, S.*; Sakuraba, Junji*; Kato, Takanori*; Okumura, Yoshikazu
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02B107_1 - 02B107_3, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:42.95(Instruments & Instrumentation)High current hydrogen negative ion source is required to increase the accelerated beam current of the cyclotrons for many medical applications such as cancer therapy and medical radioisotope production. A new negative ion source has been designed and fabricated. The ion source is a multi-cusp type. Optimization of the ion source is in progress, such as the optimization of the magnetic filter which prevents high temperature electrons from entering into the negative ion production region, improvement of the extraction electrode's shape and configuration of dipole magnets etc. A small quantity of Cs has been introduced into the ion source to enhance the negative ion beam current. The ion source produced 16mA of DC hydrogen negative ion beam with the Cs-seeded operation at a low arc discharge power of 2.8 kW.
Sakaki, Hironao; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Maeda, Shota; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A.*; Ogura, Koichi; Fukami, Tomoyo; Matsukawa, Kenya*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02A705_1 - 02A705_4, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.24(Instruments & Instrumentation)High intensity laser-plasma interaction has attracted considerable interest for a number of years. The laser-plasma interaction is accompanied by generation of various charged particle beams. Results of simultaneous novel measurements of electron-induced photonuclear neutrons (photoneutron), which are a diagnostic of the laser-plasma interaction, are proposed to use for optimization of the laser-plasma ion generation. The proposed method is demonstrated by the laser irradiation with the intensity os 1 10
10 W/cm
W/cm on the metal foil target. The photoneutrons are measured by using NE213 liquid scintillation detectors. Heavy-ion signal is registered with the CR39 track detector simultaneously. The measured signals of the electron-induced photoneutrons are well reproduced by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). The results obtained provide useful approach for analyzing the various laser based ion beams.
on the metal foil target. The photoneutrons are measured by using NE213 liquid scintillation detectors. Heavy-ion signal is registered with the CR39 track detector simultaneously. The measured signals of the electron-induced photoneutrons are well reproduced by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). The results obtained provide useful approach for analyzing the various laser based ion beams.